Wind energy is short for the conversion of energy captured from wind to electrical or mechanical energy. Wind power turbines produce electrical energy and windmills produce mechanical energy. Other forms for wind energy conversion are wind pumps which use wind energy to pump water or sails which drive sail boats.
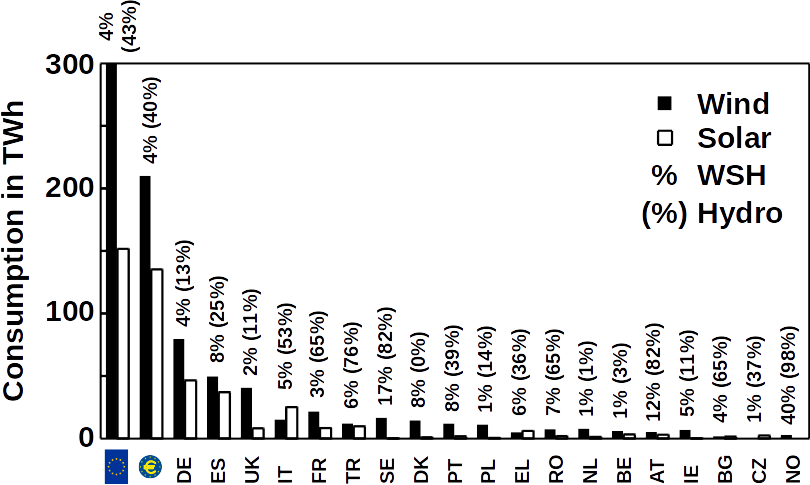
Since its first use on sail boats, wind energy is wide spread. Windmills have been used for more than 2,000 years as source of mechanical energy. The Scotsman James Blythe was the first who demonstrated the transformation of wind energy into electrical energy. As wind energy is a renewable source of energy, electrical energy generated by wind turbines is a clean and sustainable form of energy. Wind energy is often also cheaper than natural gas, for example throughout the entire American Midwest, as shown by the Energy Institute of University of Texas, Austin. It is therefore not surprising that wind energy is one of the fastest growing markets in the renewable energy sector worldwide. In 2015, 38% of all renewable energy in the United States and the European Union was generated by wind turbines.
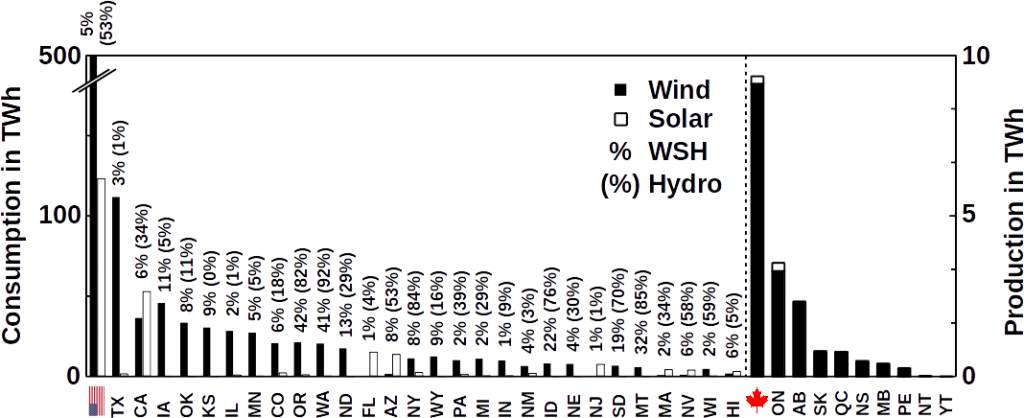
More efficient than single wind turbines is the use of wind parks where clusters of large turbines constantly generate electrical power. There are two kinds of wind parks, on-shore and off-shore wind parks. Off-shore wind parks are often more expensive but do not use valuable farmland as it is often the case for on-shore wind parks. However, wind parks on farmland can be a valuable addition for farmers seeking an extra income.
This post is also available in Deutsch.